Product Description
Los accesorios neumáticos, especialmente las tuberías y acoples son necesarios en un sistema con presión neumática!
Los Accesorios Neumáticos mantienen su función de conectar las diferentes partes para transferir la energía de presión o para reducir el ruido desde el sistema neumático, de manera que los sistemas pueden trabajar sin problemas y sin ruido.
RTQD dispone de un amplia gama de accesorios neumáticos para diferentes situaciones, tenemos diferentes tipos de acoples plásticos, acoples metálicos, conectores neumáticos, etc.
Fabricamos componentes neumáticos para el mercado de Equipo Original, y suministramos CHINAMFG tipo de accesorios neumáticos para muchos fabricantes Chinos y de diferentes países.
Especificación
Nuestro Producto
Aplicación
Fábrica
Paquete y TransportePagoFAQ
| Material: | Aluminum |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Print, Semiconductor, Automation and Control, Robot |
| Structure: | General Cylinder |
| Power: | Pneumatic |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Pressure Direction: | Double-acting Cylinder |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can rotary cylinders be employed in material handling equipment for rotational tasks?
Yes, rotary cylinders can be employed in material handling equipment for rotational tasks. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Material handling equipment encompasses a wide range of machinery used for the movement, positioning, and manipulation of materials in various industries. Rotary cylinders are well-suited for performing rotational tasks in material handling applications. Here’s how they are employed:
1. Rotational Motion Generation: Rotary cylinders convert fluid power, either hydraulic or pneumatic, into rotary motion. They can provide the necessary torque and rotational force to rotate or manipulate materials. By controlling the fluid flow to the cylinder, the rotational motion can be precisely regulated, allowing for controlled and accurate handling of materials.
2. Load Manipulation: Rotary cylinders can be used to manipulate loads by rotating them to a desired position or orientation. For example, in manufacturing processes, rotary cylinders can be employed to rotate workpieces for machining, assembly, or inspection purposes. In warehouse or logistics applications, they can be used to rotate pallets, containers, or other materials for loading, unloading, or sorting operations.
3. Angular Positioning: Rotary cylinders enable angular positioning of materials with high accuracy. They can rotate objects to specific angles or index them at precise intervals. This capability is crucial in applications that require precise alignment or positioning of materials, such as aligning components for assembly or positioning items on conveyor systems.
4. Synchronization with Other Equipment: Rotary cylinders can be seamlessly integrated with other material handling equipment to achieve synchronized rotational tasks. For example, they can be coupled with conveyors, robotic arms, or grippers to rotate or position materials as part of a coordinated handling process. This integration enhances the overall efficiency and productivity of material handling operations.
5. Control and Adjustability: Rotary cylinders offer precise control over the rotational motion, allowing for adjustments based on the specific requirements of the material handling task. The rotational speed, acceleration, and stopping position can be accurately controlled, ensuring safe and efficient material manipulation. This control and adjustability contribute to optimized handling operations and improved productivity.
6. Compact and Lightweight Design: Rotary cylinders are often designed to be compact and lightweight, making them suitable for integration into material handling equipment. Their compact size allows for efficient use of space, while their lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of the equipment. This design characteristic facilitates faster response times, reduces inertia, and enhances the overall performance and maneuverability of the material handling equipment.
7. Customization: Manufacturers offer a wide range of rotary cylinder models with different sizes, load capacities, and performance characteristics. This allows users to select the most suitable cylinder for their specific material handling application. Customization options further enhance the ability to tailor the cylinder’s performance to meet the rotational requirements of different materials and tasks.
8. Safety Features: Rotary cylinders can incorporate safety features to ensure secure material handling. These features may include position sensing devices, limit switches, or torque sensors that detect abnormal conditions or prevent excessive forces during rotation. Safety mechanisms help protect the materials being handled, prevent damage to the equipment, and ensure the safety of operators.
By incorporating these features and considerations, rotary cylinders serve as valuable components in material handling equipment, enabling efficient and precise rotational tasks for a wide range of materials and applications.
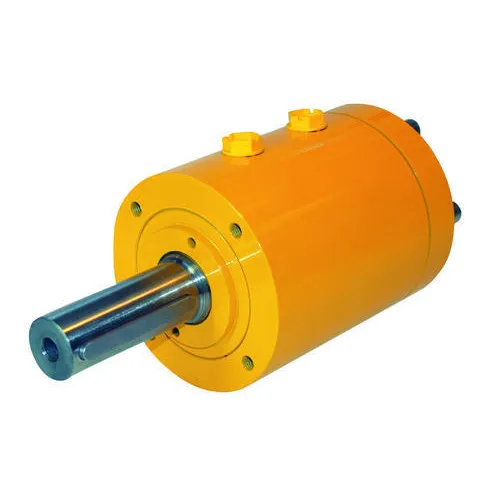

How do rotary cylinders contribute to energy-efficient equipment operation?
Rotary cylinders play a significant role in promoting energy-efficient equipment operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power-On-Demand: Rotary cylinders operate based on fluid power, either hydraulic or pneumatic. One of the key advantages of fluid power systems is their power-on-demand capability. This means that the cylinder generates force and consumes energy only when necessary to perform a specific task. When the task is completed, the fluid flow to the cylinder can be shut off, resulting in energy savings compared to continuously running mechanical systems.
2. Efficient Force Conversion: Rotary cylinders efficiently convert fluid power into rotary motion. They can generate high torque, enabling them to perform tasks requiring substantial rotational force. The efficient force conversion minimizes energy losses during operation, allowing for effective utilization of input energy to achieve desired movements and work output.
3. Compact Design: Rotary cylinders are often designed to be compact and lightweight. This design approach reduces the overall weight and inertia of the equipment, resulting in energy savings. The reduced weight requires less energy to accelerate and decelerate the moving parts of the equipment, leading to improved energy efficiency.
4. Precise Control: Rotary cylinders offer precise control over the rotational motion. The ability to control speed, acceleration, and position with accuracy allows for optimized equipment operation. By fine-tuning the control parameters, energy consumption can be minimized while still achieving the desired performance. This precise control contributes to energy-efficient operation by avoiding unnecessary energy wastage.
5. Integration with Control Systems: Rotary cylinders can be seamlessly integrated into control systems such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or computer numerical control (CNC) systems. These control systems enable advanced algorithms and optimization techniques to be applied to the operation of rotary cylinders. By optimizing the control signals and adjusting parameters in real-time, energy consumption can be further reduced while maintaining the required functionality.
6. Energy Recovery: In certain applications, rotary cylinders can incorporate energy recovery systems. These systems capture and utilize the energy released during deceleration or load lowering. For example, in hydraulic systems, energy recovery can be achieved through the use of regenerative valves or accumulators, which store and reuse the energy that would otherwise be dissipated as heat. By recovering and reusing energy, overall energy efficiency is improved.
7. System Optimization: Rotary cylinders are part of larger systems and equipment. By considering the overall system design and optimizing the interaction between components, energy-efficient operation can be achieved. This may involve optimizing the sizing and selection of rotary cylinders, reducing friction and leakage losses, implementing efficient fluid distribution systems, and employing energy-efficient control strategies.
8. Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring and maintenance of rotary cylinders contribute to energy-efficient equipment operation. By detecting and addressing issues such as leaks, wear, or misalignment, the performance and efficiency of the cylinders can be maintained. Proper lubrication and alignment also reduce energy losses and ensure smooth operation.
By incorporating these features and considerations, rotary cylinders contribute to energy-efficient equipment operation, reducing energy consumption, and promoting sustainability in various industries.
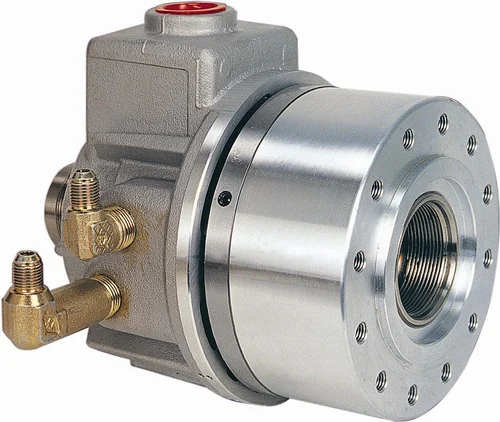
Can rotary cylinders be used for both rotary motion and linear motion?
No, rotary cylinders are specifically designed for generating rotary motion and are not typically used for linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Rotary Motion:
Rotary cylinders, also known as rotary actuators, are primarily used to convert fluid power into rotational motion. They are designed to generate torque and rotate around a central axis. The rotational movement can be in a full 360-degree rotation or limited to a specific angle depending on the application and the design of the cylinder.
Linear Motion:
For linear motion, a different type of actuator, such as linear cylinders or linear actuators, is used. Linear cylinders are specifically designed to generate linear motion by extending or retracting a piston rod in a linear path. These actuators are commonly used in applications where straight-line movement is required, such as pushing, pulling, lifting, or sliding objects.
Differences:
The design and internal mechanism of rotary cylinders are optimized for rotational motion, while linear cylinders are designed to provide linear motion. These two types of actuators have different structures and operating principles to fulfill their respective purposes.
While rotary cylinders cannot directly produce linear motion, they can be part of a system that combines both rotary and linear motion. For example, in some applications, a rotary cylinder can be used to generate rotational motion, which is then converted into linear motion using additional mechanisms such as racks, gears, or linkages.
It’s important to choose the appropriate type of actuator based on the desired motion requirements of the specific application. Manufacturers’ documentation and guidelines should be consulted to determine the most suitable actuator for a particular motion requirement.

editor by CX 2023-11-29