Product Description
0.2L oxygen Aluminum Cylinder
Main Feature:
Model Number: LW-50-0.2-200
water capacity 0.2L
Standard:GB11640-2011(Aluminum6061)
Thickness of seamless:3.4+0.5mm
Diameter:50mm
Height: 185mm
working pressure:200bar
test pressure: 300bar
Cylinders are made from high strength Aluminum Alloy 6061, reliable in durability, fracture toughness and resistance to tearing and cracking.
Highly corrosion-resistant interior and exterior-ideal for wet gases.
Cylinders perform well at low temperatures.
Lightweight–up to 40 percent lighter than comparable steel cylinders and in Consistent weight, consistent thickness resist damage.
Brushed external surface provides a low-maintenance finish.
Cylinders meet or exceed all regulatory standards worldwide.
Cylinders cycle-tested in excess of 120,000 cycles at service pressure. Excess of 12000 cycles at test pressure.
Minimum burst pressure tested to 2.5 times service pressure without failure.
* Valve & Threads can be specified & installed CHINAMFG Request.
* Standard Finishing is RAL300 Red Powder Coated.
* Markings according to Standard Specifications, Additional Markings Available Ipon Request.
certificate:
specification:
| Type | (mm) Outside Diameter |
(L) Water Capacity |
(mm) Height (Withoutvalve) |
(Kg) Weight(Without valve,cap) |
(Mpa) Working Pressure |
(mm) Design Wall Thickness |
| LW-60-0.5-20H | 60 | 0.5 | 285 | 0.6 | 200 | 3.1 |
| LW-75-0.7-15H | 75 | 0.7 | 295 | 0.9 | 150 | 4 |
| LW-82-0.7-15H | 82 | 0.7 | 235 | 0.9 | 150 | 4.2 |
| LW-89-1.0-15H | 89 | 1.0 | 269 | 1.2 | 150 | 4.5 |
| LW-89-1.4-15H | 89 | 1.4 | 345 | 1.4 | 150 | 4.5 |
| LW-108-1.0-15H | 108 | 1.0 | 210 | 1.3 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-108-1.4-15H | 108 | 1.4 | 264 | 1.6 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-108-2.0-15H | 108 | 2.0 | 346 | 2.1 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-108-2.5-15H | 108 | 2.5 | 413 | 2.5 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-120-2.0-15H | 120 | 2.0 | 320 | 2.7 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-120-2.5-15H | 120 | 2.5 | 369 | 3.0 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-120-2.8-15H | 120 | 2.8 | 398 | 3.2 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-120-3.2-15H | 120 | 3.2 | 437 | 3.5 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-140-4.0-15H | 140 | 4.0 | 420 | 4.2 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-5.0-15H | 140 | 5.0 | 500 | 4.9 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-6.0-15H | 140 | 6.0 | 580 | 5.6 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-8.0-15H | 140 | 8.0 | 741 | 7.2 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-5.0-20H | 140 | 5.0 | 525 | 6.3 | 200 | 9.3 |
| LW-140-6.0-20H | 140 | 6.0 | 652 | 7.98 | 200 | 9.3 |
| LW-159-10.0-15H | 159 | 10.0 | 730 | 8.8 | 150 | 8 |
| LW-184-9.0-20H | 184 | 9.0 | 575 | 12.0 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-184-10.0-20H | 184 | 10.0 | 620 | 12.9 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-184-11.0-20H | 184 | 11.0 | 665 | 14.2 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-184-12.0-20H | 184 | 12.0 | 710 | 15.4 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-203-12-15H | 203 | 12.0 | 567 | 11.8 | 150 | 10.3 |
| LW-203-15-15H | 203 | 20.0 | 873 | 17.0 | 150 | 10.3 |
| LW-203-21.3-15H | 203 | 21.3 | 962 | 19.9 | 150 | 10.3 |
| LW-204-12-20H | 204 | 12.0 | 610 | 16.5 | 200 | 13.4 |
| LW-204-15-20H | 204 | 15.0 | 735 | 18.7 | 200 | 13.4 |
| LW-204-20-20H | 204 | 20.0 | 940 | 23.4 | 200 | 13.4 |
| LW-232-29.5-15H | 232 | 29.5 | 994 | 30.2 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-30.3-15H | 232 | 30.0 | 1571 | 30.5 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-33.4-15H | 232 | 33.4 | 1126 | 31.3 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-40.0-15H | 232 | 40.0 | 1340 | 36.5 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-20.0-20H | 232 | 20.0 | 750 | 26.9 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-26.0-20H | 232 | 26.0 | 921 | 30.7 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-30.0-20H | 232 | 30.0 | 1076 | 36.4 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-31.5-20H | 232 | 31.5 | 1096 | 38.0 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-40.0-20H | 232 | 40.0 | 1365 | 44.1 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-250-40.0-15H | 250 | 40.0 | 1150 | 36.7 | 150 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-46.4-15H | 250 | 46.4 | 1305 | 38.7 | 150 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-47.5-15H | 250 | 47.5 | 1340 | 42.0 | 150 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-50.0-15H | 250 | 50.0 | 1590 | 39.0 | 200 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-40.0-20H | 250 | 40.0 | 1227 | 46.3 | 200 | 16.5 |
| LW-250-50.0-20H | 250 | 50.0 | 1500 | 56.0 | 200 | 16. |
Company profile:
Our factory aluminium jar-making co.,ltd. is a professional filter capacitor shell aluminum shell and the development and production of a wholly-owned enterprise. Founded in 1988, now covers an area of 80,000 square meters, staff 320 people, including engineers and technicians 25 people. Since its inception, that is fully committed to the manufacture of aluminum cans , aluminum semi-finished products processing and metallurgy and processing such as special-shaped parts, with a strong technical force and good quality staff, and constantly develop new products, develop new markets,
Growing scale of production. Products not only meet the domestic demand, but also exported to Europe, America and Southeast Asia regions, well received by customers and vendors praise!
Company’s existing 3 series of products, Capacitor aluminum shell and cover, fuel filter housing and shelters, EFI pump casing. The company pays great attention to product quality, strictly follow the concept of lean production and methods of management of production. And has achieved ISO9001:2008quality system.certification.ISO14001:2004, EN ISO7866:2012+AC2014 environmental management system certification and ISO/TS16949: 2009auto parts industry certification.
The company in line to provide customers with the fastest, most comprehensive and efficient services for the purpose, sincerely welcome friends home and abroad to write to.
| Function: | Storage Pressure Vessel |
|---|---|
| Application: | Gas |
| Pressure: | 10.0MPa≤p<100.0MPa |
| Storage Medium: | Oxygen |
| Pressure Level: | High Pressure (10.0MPa≤p<100.0MPa) |
| Condition: | New |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have improved sealing and reliability?
Advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have continuously contributed to improving sealing and reliability in hydraulic systems. These advancements aim to address common challenges such as leakage, wear, and failure of seals, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are several key advancements that have significantly improved sealing and reliability in hydraulic cylinders:
1. High-Performance Sealing Materials:
– The development of advanced sealing materials has greatly improved the sealing capabilities of hydraulic cylinders. Traditional sealing materials like rubber have been replaced or enhanced with high-performance materials such as polyurethane, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), and various composite materials. These materials offer superior resistance to wear, temperature, and chemical degradation, resulting in improved sealing performance and extended seal life.
2. Enhanced Seal Designs:
– Advancements in seal designs have focused on improving sealing efficiency and reliability. Innovative seal profiles, such as lip seals, wipers, and scrapers, have been developed to optimize fluid retention and prevent contamination. These designs provide better sealing performance, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage and maintaining system integrity. Additionally, improved seal geometries and manufacturing techniques ensure tighter tolerances, reducing the potential for seal failure due to misalignment or extrusion.
3. Integrated Seal and Bearing Systems:
– Hydraulic cylinders now incorporate integrated seal and bearing systems, where the sealing elements also serve as bearing surfaces. This design approach reduces the number of components and potential failure points, improving overall reliability. By integrating seals and bearings, the risk of seal damage or displacement due to excessive loads or misalignment is minimized, resulting in enhanced sealing performance and increased reliability.
4. Advanced Coatings and Surface Treatments:
– The application of advanced coatings and surface treatments to hydraulic cylinder components has significantly improved sealing and reliability. Coatings such as chrome plating or ceramic coatings enhance surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. These surface treatments provide a smoother and more durable surface for seals to operate against, reducing friction and improving sealing performance. Moreover, specialized coatings can also provide self-lubricating properties, reducing the need for additional lubrication and enhancing reliability.
5. Sealing System Monitoring and Diagnostic Technologies:
– The integration of monitoring and diagnostic technologies in hydraulic systems has revolutionized seal performance and reliability. Sensors and monitoring systems can detect and alert operators to potential seal failures or leaks before they escalate. Real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and seal performance parameters allows for proactive maintenance and early intervention, preventing costly downtime and ensuring optimal sealing and reliability.
6. Computational Modeling and Simulation:
– Computational modeling and simulation techniques have played a significant role in advancing hydraulic cylinder sealing and reliability. These tools enable engineers to analyze and optimize seal designs, fluid flow dynamics, and contact stresses. By simulating various operating conditions, potential issues such as seal extrusion, wear, or leakage can be identified and mitigated early in the design phase, resulting in improved sealing performance and enhanced reliability.
7. Systematic Maintenance Practices:
– Advances in hydraulic cylinder technology have also emphasized the importance of systematic maintenance practices to ensure sealing and overall system reliability. Regular inspection, lubrication, and replacement of seals, as well as routine system flushing and filtration, help prevent premature seal failure and optimize sealing performance. Implementing preventive maintenance schedules and adhering to recommended service intervals contribute to extended seal life and enhanced reliability.
In summary, advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have led to significant improvements in sealing and reliability. High-performance sealing materials, enhanced seal designs, integrated seal and bearing systems, advanced coatings and surface treatments, sealing system monitoring and diagnostics, computational modeling and simulation, and systematic maintenance practices have all played key roles in achieving optimal sealing performance and increased reliability. These advancements have resulted in more efficient and dependable hydraulic systems, minimizing leakage, wear, and failure of seals, and ultimately improving the overall performance and longevity of hydraulic cylinders in diverse applications.

Can you provide real-world examples of machinery that heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders?
Hydraulic cylinders are widely used in various industries and applications due to their ability to provide powerful and precise linear motion. They play a crucial role in enabling the operation of heavy machinery that requires controlled force and movement. Here are some real-world examples of machinery that heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders:
1. Construction Equipment:
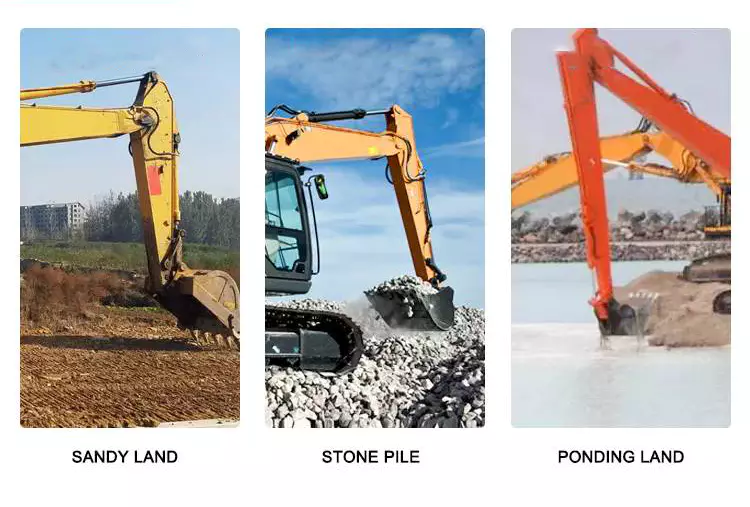
– Hydraulic cylinders are extensively used in construction machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and cranes. These machines rely on hydraulic cylinders to perform tasks like lifting heavy loads, extending and retracting booms, tilting buckets, and controlling the movement of various components. Hydraulic cylinders provide the power and precision required to handle the demanding conditions and heavy loads encountered in construction projects.
2. Agricultural Machinery:
– Many agricultural machines, including tractors, combine harvesters, and sprayers, utilize hydraulic cylinders for critical operations. Hydraulic cylinders are used to control the movement of attachments, such as front loaders, backhoes, and plows. They enable functions like lifting and lowering implements, adjusting cutting heights, and controlling the positioning of harvesting equipment. Hydraulic cylinders enhance efficiency and productivity in agricultural operations.
3. Material Handling Equipment:
– Hydraulic cylinders are integral components of material handling equipment, such as forklifts, pallet jacks, and cranes. These machines rely on hydraulic cylinders to lift and lower loads, tilt platforms or forks, and control the movement of lifting mechanisms. Hydraulic cylinders provide the necessary strength and precision to handle heavy loads and ensure safe and efficient material handling operations.
4. Industrial Machinery:
– Various industrial machinery and equipment heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders for critical functions. Examples include hydraulic presses, injection molding machines, metal-forming machines, and hydraulic-powered robots. Hydraulic cylinders enable precise control of force and movement in these applications, allowing for accurate shaping, pressing, and assembly processes.
5. Mining Equipment:
– Hydraulic cylinders are extensively used in mining machinery and equipment. Underground mining machines, such as continuous miners and longwall shearers, utilize hydraulic cylinders for cutting, shearing, and roof support operations. Surface mining equipment, including hydraulic shovels, draglines, and haul trucks, rely on hydraulic cylinders for tasks like bucket movement, boom extension, and vehicle suspension.
6. Automotive Industry:
– The automotive industry extensively utilizes hydraulic cylinders in various applications. Hydraulic cylinders are employed in vehicle suspension systems, power steering systems, convertible tops, and hydraulic brake systems. They enable smooth and controlled movement, precise steering, and efficient braking in automobiles.
7. Aerospace and Aviation:
– Hydraulic cylinders are utilized in aerospace and aviation applications, such as aircraft landing gear systems, wing flaps, and cargo handling equipment. Hydraulic cylinders provide the necessary force and control for extending and retracting landing gear, adjusting wing flaps, and operating cargo doors, ensuring safe and reliable aircraft operations.
8. Marine and Offshore Industry:
– Hydraulic cylinders are essential components in marine and offshore equipment, including ship cranes, winches, and hydraulic-powered anchor systems. They enable lifting, lowering, and positioning of heavy loads, as well as the control of various marine equipment.
These are just a few examples of machinery and industries that heavily rely on hydraulic cylinders. The versatility, power, and precise control offered by hydraulic cylinders make them indispensable in a wide range of applications, where controlled linear motion and force are essential.

How do hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion using hydraulic fluid?
Hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion by utilizing the principles of fluid mechanics, specifically Pascal’s law, in conjunction with the properties of hydraulic fluid. The process involves the conversion of hydraulic energy into mechanical force and linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders achieve this:
1. Pascal’s Law:
– Hydraulic cylinders operate based on Pascal’s law, which states that when pressure is applied to a fluid in a confined space, it is transmitted equally in all directions. In the context of hydraulic cylinders, this means that when hydraulic fluid is pressurized, the force is evenly distributed throughout the fluid and transmitted to all surfaces in contact with the fluid.
2. Hydraulic Fluid and Pressure:
– Hydraulic systems use a specialized fluid, typically hydraulic oil, as the working medium. This fluid is stored in a reservoir and circulated through the system by a hydraulic pump. The pump pressurizes the fluid, creating hydraulic pressure that can be controlled and directed to various components, including hydraulic cylinders.
3. Cylinder Design and Components:
– Hydraulic cylinders consist of several key components, including a cylindrical barrel, a piston, a piston rod, and various seals. The barrel is a hollow tube that houses the piston and allows for fluid flow. The piston divides the cylinder into two chambers: the rod side and the cap side. The piston rod extends from the piston and provides a connection point for external loads. Seals are used to prevent fluid leakage and maintain hydraulic pressure within the cylinder.
4. Fluid Input and Motion:
– To generate force and motion, hydraulic fluid is directed into one side of the cylinder, creating pressure on the corresponding surface of the piston. This pressure is transmitted through the fluid to the other side of the piston.
5. Force Generation:
– The force generated by a hydraulic cylinder is a result of the pressure applied to a specific surface area of the piston. The force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder can be calculated using the formula: Force = Pressure × Area. The area is determined by the diameter of the piston or the piston rod, depending on which side of the cylinder the fluid is acting upon.
6. Linear Motion:
– As the pressurized hydraulic fluid acts on the piston, it generates a force that moves the piston in a linear direction within the cylinder. This linear motion is transferred to the piston rod, which extends or retracts accordingly. The piston rod can be connected to external components or machinery, allowing the generated force to perform various tasks, such as lifting, pushing, pulling, or controlling mechanisms.
7. Control and Regulation:
– The force and motion generated by hydraulic cylinders can be controlled and regulated by adjusting the flow of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. By regulating the flow rate, pressure, and direction of the fluid, the speed, force, and direction of the cylinder’s movement can be precisely controlled. This control allows for accurate positioning, smooth operation, and synchronization of multiple cylinders in complex machinery.
8. Return and Recirculation of Fluid:
– After the hydraulic cylinder completes its stroke, the hydraulic fluid on the opposite side of the piston needs to be returned to the reservoir. This is typically achieved through hydraulic valves that control the flow direction, allowing the fluid to return and be recirculated in the system for further use.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion by utilizing the principles of Pascal’s law. Pressurized hydraulic fluid acts on the piston, creating force that moves the piston in a linear direction. This linear motion is transferred to the piston rod, allowing the generated force to perform various tasks. By controlling the flow of hydraulic fluid, the force and motion of hydraulic cylinders can be precisely regulated, contributing to their versatility and wide range of applications in machinery.

editor by CX 2023-11-21