Product Description
Dryer Cylinder
The dryer cylinder for paper machine is a key part of paper drying.
It is used in drying part of a paper production line. Working with hot steam from steam boiler, dryer cylinder dry wet paper sheets, then the dry paper sheets can be reeled into jumbo rolls.
The function of the dryer is to dry the moisture in the paper and finish the paper surface.
Dryer Cylinder Spare Parts
Dryer Cylinder Turbulators
The purpose of the turbulators is to destroy the condensation water ring formed in the dryer at high speed and generate more turbulence. The turbulators is installed on the inner surface of the dryer. It rotates with the dryer at the same speed, so it will move the water ring to produce turbulence, which is conducive to heat conduction.
Separate design, with light weight, and convenient and quick forinstallation.
High radial and axial strength in overall structure.
Ensuring maximum instaation firmness.
Dryer cylinder Siphon
In order to ensure the smooth discharge of condensed water in the dryer and avoid flooding; Make the cylinder surface temperature as high as possible to improve the drying efficiency; In order to reduce the temperature difference on the cylinder surface and make the moisture content of the paper uniform, the selection of siphon becomes the key.
Dryer drainage siphon is basically divided into 2 forms: fixed type and rotary type. The fixed siphon is fixed on a certain point outside the dryer and does not rotate with the dryer; The rotary siphon is fixed in the dryer and rotates with the dryer.
Dryer Cylinder Rotary Joint
The dryer needs steam, and the internal condensate needs to be discharged. But the dryer is a rotating cylinder, so a special joint is needed to complete this task, that is, the steam joint.
Steam in and condensate out are usually completed by a rotary joint at 1 end of the dryer, or steam in and condensate out at 1 end.
Production Parameter
| Diameter (mm) |
Design Pressure (MPa) |
Material | Hardness HB |
Web Width (mm) |
Shell Thickness (mm) |
Roughness | Working Speed (m/min) |
| 1500 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 350-1000 | 20-30 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-1200 |
| 1800 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 350-1000 | 23-35 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-1200 |
| 2000 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 1350-5000 | 24-38 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-1200 |
| 2500 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 1350-5000 | 24-46 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-500 |
| 3000 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 1350-5000 | 28-54 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-600 |
| 3660 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 1350-5000 | 33-65 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-1200 |
| 3680 | 0.3-0.8 | HT250-300 | 190-240 | 1350-5000 | 33-65 | 0.2-0.4 | 200-1200 |
| After-sales Service: | Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Certification: | ISO 9001:2000, ISO 9001:2008 |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Cast Iron |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
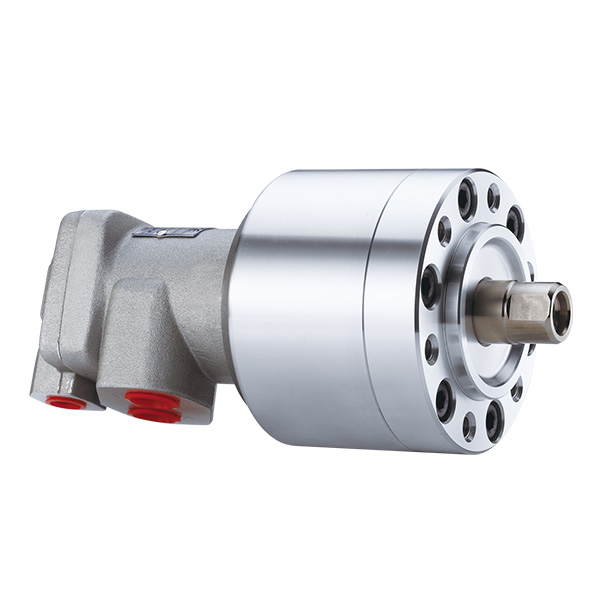

What safety considerations are important when working with machinery equipped with rotary cylinders?
Working with machinery equipped with rotary cylinders requires careful attention to safety to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of operators and bystanders. Here are important safety considerations to keep in mind:
1. Hazard Identification: Identify potential hazards associated with the machinery and its rotary cylinders. This includes understanding the risks posed by rotating parts, high-pressure fluid systems, pinch points, and potential entanglement hazards.
2. Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to evaluate the potential risks and their severity. Identify measures to mitigate risks and prioritize safety controls accordingly.
3. Safety Guards and Enclosures: Install appropriate safety guards and enclosures to prevent access to hazardous areas, such as rotating components or fluid lines. Ensure that these guards are securely in place and cannot be easily bypassed.
4. Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Develop and enforce lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that machinery equipped with rotary cylinders is properly shut down and de-energized during maintenance or repair activities. This prevents unexpected movement of the cylinders and the potential for injury.
5. Training and Competence: Provide comprehensive training to operators and maintenance personnel on the safe operation of machinery equipped with rotary cylinders. Ensure that they are competent in identifying hazards, understanding safety procedures, and implementing safe work practices.
6. Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Implement a routine maintenance program to keep the machinery and rotary cylinders in good working condition. Regularly inspect the cylinders, fluid lines, fittings, and connections for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Replace any faulty components promptly.
7. Pressure Relief and Emergency Stop Systems: Install pressure relief valves and emergency stop systems to safely control and halt the operation of machinery in case of emergencies or unexpected events.
8. Warning Signs and Labels: Clearly display warning signs and labels to communicate potential hazards and safety instructions related to the machinery equipped with rotary cylinders. Ensure that operators and other personnel are aware of and understand these warnings.
9. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing, to operators and maintenance personnel. PPE should be used in accordance with relevant safety standards and risk assessments.
10. Continuous Safety Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous safety improvement by encouraging reporting of near misses, conducting regular safety audits, and addressing any identified safety concerns promptly.
It’s essential to comply with local safety regulations and industry standards specific to the machinery and applications using rotary cylinders. Additionally, consult manufacturers’ documentation and guidelines for specific safety considerations related to the rotary cylinders used in the machinery.
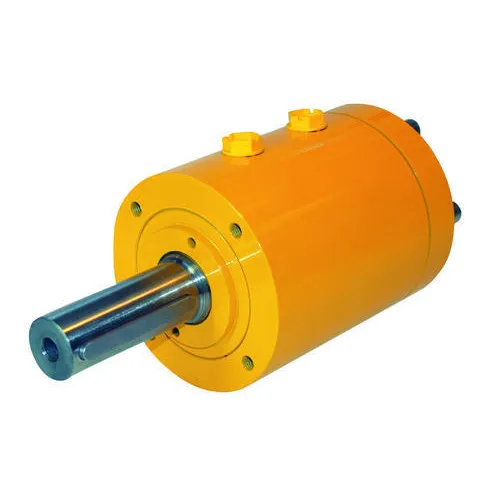

How do rotary cylinders contribute to energy-efficient equipment operation?
Rotary cylinders play a significant role in promoting energy-efficient equipment operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power-On-Demand: Rotary cylinders operate based on fluid power, either hydraulic or pneumatic. One of the key advantages of fluid power systems is their power-on-demand capability. This means that the cylinder generates force and consumes energy only when necessary to perform a specific task. When the task is completed, the fluid flow to the cylinder can be shut off, resulting in energy savings compared to continuously running mechanical systems.
2. Efficient Force Conversion: Rotary cylinders efficiently convert fluid power into rotary motion. They can generate high torque, enabling them to perform tasks requiring substantial rotational force. The efficient force conversion minimizes energy losses during operation, allowing for effective utilization of input energy to achieve desired movements and work output.
3. Compact Design: Rotary cylinders are often designed to be compact and lightweight. This design approach reduces the overall weight and inertia of the equipment, resulting in energy savings. The reduced weight requires less energy to accelerate and decelerate the moving parts of the equipment, leading to improved energy efficiency.
4. Precise Control: Rotary cylinders offer precise control over the rotational motion. The ability to control speed, acceleration, and position with accuracy allows for optimized equipment operation. By fine-tuning the control parameters, energy consumption can be minimized while still achieving the desired performance. This precise control contributes to energy-efficient operation by avoiding unnecessary energy wastage.
5. Integration with Control Systems: Rotary cylinders can be seamlessly integrated into control systems such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or computer numerical control (CNC) systems. These control systems enable advanced algorithms and optimization techniques to be applied to the operation of rotary cylinders. By optimizing the control signals and adjusting parameters in real-time, energy consumption can be further reduced while maintaining the required functionality.
6. Energy Recovery: In certain applications, rotary cylinders can incorporate energy recovery systems. These systems capture and utilize the energy released during deceleration or load lowering. For example, in hydraulic systems, energy recovery can be achieved through the use of regenerative valves or accumulators, which store and reuse the energy that would otherwise be dissipated as heat. By recovering and reusing energy, overall energy efficiency is improved.
7. System Optimization: Rotary cylinders are part of larger systems and equipment. By considering the overall system design and optimizing the interaction between components, energy-efficient operation can be achieved. This may involve optimizing the sizing and selection of rotary cylinders, reducing friction and leakage losses, implementing efficient fluid distribution systems, and employing energy-efficient control strategies.
8. Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring and maintenance of rotary cylinders contribute to energy-efficient equipment operation. By detecting and addressing issues such as leaks, wear, or misalignment, the performance and efficiency of the cylinders can be maintained. Proper lubrication and alignment also reduce energy losses and ensure smooth operation.
By incorporating these features and considerations, rotary cylinders contribute to energy-efficient equipment operation, reducing energy consumption, and promoting sustainability in various industries.

How does a rotary cylinder differ from other types of hydraulic cylinders?
A rotary cylinder differs from other types of hydraulic cylinders in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Principle of Operation:
A rotary cylinder is designed to convert fluid power into rotational motion, while other types of hydraulic cylinders primarily provide linear motion. While standard hydraulic cylinders extend and retract in a straight line, a rotary cylinder generates rotary or swinging motion.
Mechanism:
Rotary cylinders utilize different mechanisms to produce rotary motion. They may employ rack-and-pinion mechanisms, vane mechanisms, or gear mechanisms, depending on the specific design. In contrast, other types of hydraulic cylinders typically use a piston and cylinder arrangement to generate linear motion.
Direction of Motion:
Rotary cylinders produce rotational motion around a fixed axis or pivot point. The direction of rotation can be clockwise or counterclockwise, depending on the design and configuration of the cylinder. In contrast, other hydraulic cylinders provide linear motion in a straight line, either extending or retracting along the axis of the cylinder.
Applications:
Rotary cylinders are commonly used in applications where rotational movement is required, such as rotary indexing tables, robotic arms, and conveyor systems. They are suitable for tasks that involve swinging, rotating, or indexing motions. On the other hand, other types of hydraulic cylinders are used in applications that primarily require linear motion, such as lifting, pushing, or pulling.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Rotary cylinders offer certain advantages over other types of hydraulic cylinders. They provide compact and efficient means of generating rotary motion, allowing for versatile applications. Rotary cylinders can deliver high torque output and precise control over rotational motion. However, one potential disadvantage is that they may have a more complex design and require additional components compared to standard hydraulic cylinders.
Fluid Medium:
Rotary cylinders can be powered by either hydraulic fluid or compressed air, depending on the specific design and application. Other types of hydraulic cylinders also utilize hydraulic fluid as the power medium. The choice of fluid medium depends on factors such as the desired force and speed, environmental considerations, and system requirements.
It’s important to consult the manufacturer’s documentation and guidelines for specific information on the selection, installation, and operation of rotary cylinders and other types of hydraulic cylinders for different applications.

editor by CX 2023-11-03